Table of Contents
ToggleDifferences between RS232 and RS485
RS232 and RS485 are widely recognized as standard protocols for serial communication, designed and developed by the EIA (Electronic Industries Association) / TIA (Telecommunication Industries Association).
Serial interfaces serve the essential function of enabling wireless data transmission over cables through a single path. When it comes to communication spanning distances beyond a few feet, a serial interface proves to be a highly reliable choice.
RS232 and RS485, two widely used serial communication protocols, differ in several key aspects:
| Feature | RS232 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Distance | Shorter distances, up to 50 feet | Longer distances, up to 4,000 feet |
| Immunity against Electrical Noise | More susceptible to noise and ground | More immune to noise and ground |
| Number of Devices | Point-to-point communication | Supports multi-drop and bus networks |
| Data Transmission Speed | Lower data rates, up to 115.2 kbps | Higher data rates, up to 10 Mbps |
Specifications of RS232 and RS485:
| Feature | RS232 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage System | Single-ended | Differential |
| Total Driver and Receiver in one line | 1 driver, 1 receiver | Multiple drivers, multiple receivers |
| Line Configuration | Point-to-Point | Multi-drop, Bus |
| Mode of Operation | Full Duplex | Half Duplex |
| Maximum Cable Length | Up to 50 feet | Up to 4,000 feet |
| Maximum Data Transmission Rate | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 10 Mbps |
| Typical Voltage Level | +/- 3 to +/- 15 volts | +/- 1.5 to +/- 5 volts |
| Receiver Input Resistance | 3-7 kΩ | >= 12 kΩ |
| Receiver Sensitivity | +/- 3 to +/- 15 volts | +/- 200 mV |
Communication Distance
In RS232, the maximum communication distance between a sender and a receiver is typically limited to 15 meters. However, with the use of repeaters or signal boosters, the cable length can be extended, although this may result in slower data communication speeds.
On the other hand, RS485 offers a significantly longer communication distance between the sender and receiver, reaching up to 1200 meters. This extended range makes RS485 a more favorable choice over RS232 when longer distances need to be covered in industrial automation applications.
Immunity against Electrical Noise and Ground
RS232 operates on a single-ended line technique, which works well when there is a minimal difference in ground potential between devices. However, in electrically noisy environments with varying potential levels, RS232 is more susceptible to data corruption and may experience reliability issues.
In contrast, RS485 utilizes a differential-voltage system, providing higher noise immunity. This makes RS485 more suitable for industrial automation applications where electrical noise is present. Additionally, RS485’s lower voltage operation allows for longer data transfer distances and higher data speeds compared to RS232.
Numbers of Devices
RS232 is a point-to-point communication protocol where communication occurs between two devices: a sender and a receiver. It is typically used for direct communication between two devices without the need for additional devices in the network.
On the other hand, RS485 is designed for multi-point systems, allowing multiple devices to be connected to a single transmitter. It supports a larger number of devices in a network, with up to 32 devices connected to a single transmitter.
This makes RS485 suitable for applications where multiple devices need to communicate over a shared bus or network.
Data Transmission Speed
RS232 has a data transmission speed of 1 Mbit/s over a distance of 15 meters, making it suitable for shorter distance communication. On the other hand, RS485 offers higher data transmission speeds, with up to 10 Mbit/s over a distance of 15 meters.
However, the advantage of RS485 lies in its long-distance capabilities, as it can transmit data up to 1200 meters with a speed of 100 Kbit/s.
This makes RS485 well-suited for applications that require communication over longer distances.
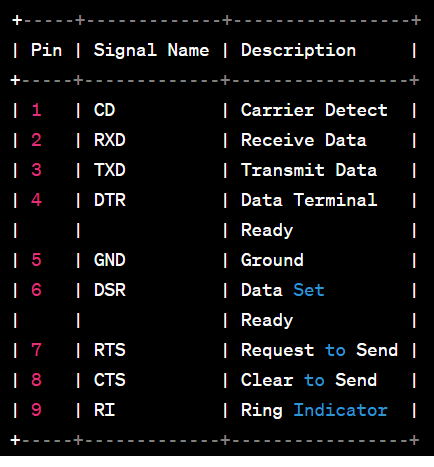
DB-9 Pin-Out Diagram

Applications
RS232 and RS485 are widely used in various applications, including:
-
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): RS232 and RS485 are commonly used for communication between PLCs and other devices in industrial automation systems.
-
Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) Machine Tools: RS232 and RS485 are employed in CNC machine tools for data transfer and control signals between the CNC controller and peripheral devices.
-
Robotics Applications: RS232 and RS485 facilitate communication between robotic systems and control devices, allowing for seamless control and coordination.
-
Embedded Control Computers: RS232 and RS485 are utilized in embedded systems for communication with external devices and sensors, enabling data exchange and control functionalities.
-
Medical Instruments: RS232 and RS485 find applications in medical instruments such as patient monitors, diagnostic equipment, and laboratory devices, enabling data transmission and control interfaces.
-
Power Measuring Instruments: RS232 and RS485 are used in power measuring instruments for data transfer and control functions in power distribution and monitoring systems.
-
Printers and Scanners: RS232 and RS485 are employed in printers, scanners, and other imaging devices for data transmission and control between the computer and the peripheral device.
Summary
RS232 offers a simple and cost-effective solution for short-distance and low-speed communication between two devices. With its two-pin full-duplex capability, it is well-suited for establishing a straightforward interface.
On the other hand, RS485 is designed to provide higher speeds over longer distances, making it suitable for network setups with multiple devices. It can support up to 32 devices in a single network and is commonly used for communication over extended distances.
We value your feedback and encourage you to share your thoughts in the comment section below if you found this article helpful or have any additional insights to contribute. Your comments are important to us.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for reading!! Happy Learning!!

