Table of Contents
ToggleTypes of Pressure Transmitters
India’s commitment to environmental sustainability is driving significant advancements in various sectors, including water treatment, reverse osmosis (RO) plants, and wastewater and effluent treatment plants. These initiatives hold immense potential for further development in the near future.
As these industries, along with water distribution networks, continue to evolve, the role of pressure sensors is becoming increasingly crucial. By incorporating pressure sensors into these processes, the systems can achieve reliability, stability, and high performance. These sensors play a vital role in ensuring quality control and system protection in wastewater and water treatment operations.
A pressure sensor is an instrumental device that converts pressure into a standard signal output, typically ranging from 4 to 20 mA.
The most commonly used measurement standard for pressure in the gas and fluid processing industry is psi/kg per sq cm/bar. The signal obtained from the pressure sensor can also be utilized to measure the liquid level of static fluids, making it applicable to water treatment and storage processes.
Pressure sensors find wide-ranging application areas, including urban water supply systems, drinking water treatment facilities, industrial sites, dam water level monitoring, and sewage treatment plants.
In this article, we will learn about practical applications of pressure transmitters and also different types of pressure sensors that can be utilized in these contexts.
Types of Pressure Transmitters
Fixed Transmitter:
The fixed pressure transmitter (FPT) is a compact instrument designed to be directly mounted on pipelines.
It operates on 24 V DC power and provides a 2-wire 4 to 20 mA current output, which can be connected to a panel-mounted digital indicator for precise measurement display and alarm functionality.
Additionally, some manufacturers offers an optional built-in display for convenient on-site readings as shown below.
The FPT is capable of accurately measuring the pressure of both gases and liquids, including corrosive substances. This versatility is achieved by carefully selecting appropriate materials for the wetted or exposed parts of the transmitter.
As a result, the fixed pressure transmitter finds extensive application in various industries, including wastewater and water treatment, pharmaceutical production, chemistry, food processing, oil and gas, laboratory research.
By utilizing the fixed pressure transmitter, industries can effectively monitor and control pressure levels in their systems. This is particularly crucial in sensitive processes where precision, reliability, and safety are paramount. With its compact design and robust performance, the FPT plays a vital role in optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring the smooth operation of critical systems across diverse industrial sectors.
Smart Pressure Transmitter
The smart pressure transmitter (SPT) is equipped with a digital display that allows for easy configuration of range settings and other parameters. Unlike the fixed pressure transmitter (FPT), the smart pressure transmitter is a variable pressure transmitter, offering more flexibility in its operation.
For Example, an SPT with a range of 0 to 10 bar can be configured to measure a range of 0 to 5 bar (4 mA at 0 bar and 20 mA at 5 bar). This adjustable range capability makes the smart pressure transmitter highly desirable for process plant applications, where different operating conditions may require specific pressure ranges.
The intelligence of the smart pressure transmitter is further enhanced by the optional inclusion of a HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) module. This feature is particularly valuable in process applications where remote range setting, configuration, and access to various smart sensor information are required.
With the HART module, operators can conveniently adjust settings and gather crucial data from the pressure transmitter without physically accessing the instrument, thus streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
The combination of a digital display, range configuration flexibility, and optional HART module makes the smart pressure transmitter an advanced and versatile instrument, capable of meeting the demands of modern industrial processes. It enables precise monitoring, control, and remote management of pressure parameters, contributing to enhanced operational performance and overall system intelligence.
Differential Pressure Transmitter
The differential pressure transmitter has gained rapid popularity and has become a preferred choice in the pressure transmitter market. It is a specialized instrument designed to measure the pressure difference between two points within a closed pipe system.
Often referred to as Delta-P or DP, where Delta represents “change in” and “P” denotes pressure, the differential pressure transmitter comprises several key components.
The DP transmitter consists of a primary component, a secondary component, and an electronic housing. The primary component includes low and high-pressure diaphragms, which are subjected to the respective pressures being measured. The secondary component is typically a basic sensor, such as a capacitance, inductance, or strain gauge element. This sensor undergoes mechanical deflection in response to the pressure difference and generates a proportional millivolt change.
The smart electronics within the transmitter then convert the millivolt change into a standardized 4 to 20 mA signal, which is directly proportional to the flow rate being measured. This conversion process allows for easy integration of the differential pressure transmitter with control systems and data acquisition devices.
The application of differential pressure transmitters is widespread in industries where flow rate measurement is crucial. They are commonly used in systems such as HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), chemical processing, oil and gas, and many others. By accurately measuring the pressure difference, differential pressure transmitters enable precise monitoring and control of flow rates, contributing to efficient process management and optimal system performance.
Due to their reliability, versatility, and ability to provide valuable flow rate data, differential pressure transmitters have experienced significant growth and have become a preferred choice for various industrial applications.
Applications of Pressure Transmitter
DP Transmitter for flow measurement
Pressure transmitters, particularly differential pressure transmitters, play a vital role in the process industry by facilitating the measurement of liquid or gas flow through pipelines. One widely employed method for flow measurement is based on measuring the pressure drop across an orifice plate installed within the pipe.
An orifice plate is a plate with a precisely sized hole located at its center. As the liquid or gas flows through the orifice, a pressure drop occurs from the upstream side to the downstream side of the plate. This pressure drop is directly proportional to the flow rate, with the relationship between flow rate and pressure drop following the square root of the pressure drop (flow rate ∝ √ΔP). By accurately measuring this pressure drop, the differential pressure transmitter can calculate the real-time flow rate within the processing pipeline.
The use of orifice plates in conjunction with differential pressure transmitters provides a reliable and widely adopted method for flow measurement in the process industry. It allows for continuous monitoring and control of flow rates, enabling operators to ensure optimal performance, detect any deviations or abnormalities, and make informed adjustments as necessary.
This flow measurement technique, facilitated by differential pressure transmitters, is applicable across various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, water and wastewater treatment, and many others. By providing accurate and real-time flow rate data, these transmitters contribute to efficient process management, resource allocation, and overall system optimization.
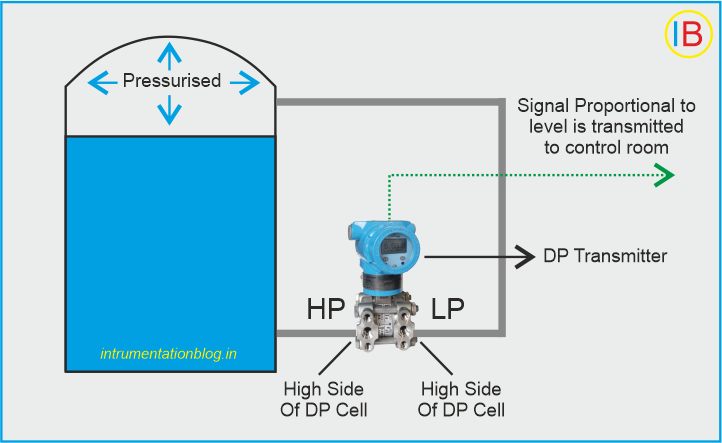
DP Transmitter for Liquid Level Measurements
Pressure sensors are versatile instruments that can also be utilized to determine the fluid level or height in process tanks. This application is commonly employed in measuring the liquid level in storage tanks such as water towers or sumps. In most practical scenarios, the liquid level exhibits a direct relationship with pressure.
The pressure level sensor used for this purpose can be either an external or submersible pressure sensor, depending on the specific requirements of the application. These sensors are designed to accurately measure the pressure at the bottom of the fluid in the tank, indirectly providing information about the fluid level.
To ensure optimal performance, it is crucial to use pressure transmitters with chemically compatible materials for contact with the fluid being measured. Additionally, accurate calibration is necessary for each application, as different liquids possess their own unique density or specific gravity.
Moreover, variations in process temperature can affect the density or specific gravity of the fluid, which must be considered during the conversion of pressure measurements into accurate level readings. Special considerations may need to be made to account for temperature changes and their impact on fluid properties.
Pressure sensors employed for level measurement can be designed to prevent contamination or accumulation on the diaphragm, thus ensuring correct operation and accurate hydrostatic pressure level measurement. By employing suitable materials, precise calibration, and accounting for temperature effects, these sensors enable reliable and accurate determination of fluid levels in storage and process tanks or reservoirs.
Refer our article on DP Transmitter for liquid level measurements.
Water Pipeline Leakage Detection
Detecting leaks in pipelines is a crucial aspect of pipeline maintenance and safety. While there are multiple methods available for leak detection, measuring the pressure within the pipeline can be an effective approach. Significant pressure reduction or fluctuations in pressure can often indicate the presence of leaks in the pipeline.

By strategically installing fixed pressure transmitters directly on the pipeline at various intervals, it becomes possible to pinpoint the specific location of a leakage along the pipeline, regardless of the type of fluid or water being transported.
These pressure transmitters continuously monitor the pressure within the pipeline, allowing for real-time detection of anomalies that may signify a leak.
The timely identification of pipeline leaks is of utmost importance as such leakages can lead to the entry of waste water into potable water lines, resulting in water contamination and potential health hazards. By promptly detecting and addressing these leaks, the risk of contamination can be mitigated, ensuring the safety and integrity of the water supply.
The use of pressure transmitters in leak detection systems provides an additional layer of protection and monitoring for pipeline networks, contributing to efficient maintenance practices, minimizing environmental impact, and safeguarding public health.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the application of pressure transmitters, including fixed pressure transmitters, smart pressure transmitters, and differential pressure transmitters, plays a crucial role in various industries and processes.
These instruments enable the accurate measurement of pressure, facilitating reliable control and monitoring of systems.
Pressure transmitters find applications in water treatment, wastewater management, industrial processes, and more.
Additionally, they are utilized for measuring flow rates, fluid levels, and detecting leaks in pipelines. With their versatility and advanced features, pressure transmitters contribute to improved efficiency, safety, and overall performance in a wide range of applications.
Their importance and impact make them essential tools in modern industrial operations.
I hope you like above blog. There is no cost associated in sharing the article in your social media. Thanks for Reading !! Happy Learning






1 Comment